SPLIT
Splits the logical files contained in an IPM file into separate physical files.
Syntax
$ cardak help split
usage: cardak split <files>...
Create phisical files from logical files present in an IPM file (a transmission)
Flags:
--help Show context-sensitive help (also try --help-long and --help-man).
-v, --verbose Add more information displayed on some commands.
--mono Supress color on output.
--ignore Try to ignore some errors and continue processing the file
-W, --width Ignore small terminal width check and force execution
-z, --silent Suppress all output (banner, headers, summary) except the results. Specially useful for DESCRIBE command piped to a search utility like fzf
Args:
<files> File names to split
Description
This command is the opposite to the JOIN command (When we don't use the --merge flag), and it takes the logical files inside a physical IPM file and writes the corresponding physical files.
This operation only makes sense when the input file contains multiple logical files (also known as transmissions), and its purpose is not to get smaller files, because if, for exmample, the original file contains two logical files, one with 200 thousand records and the second one with just 10 records, the resulting files will contain 10 and 200 thousand records, so there is not uniform distribution of data. If what is desired is to make files with a smaller size, then the correct command to use is CHOP.
The generated files are named like this: field PDS0105 (File ID) from each logical file's header, plus the date and time of the execution of the command, plus a secuential number, and adding the ".ipm" extension.
Examples
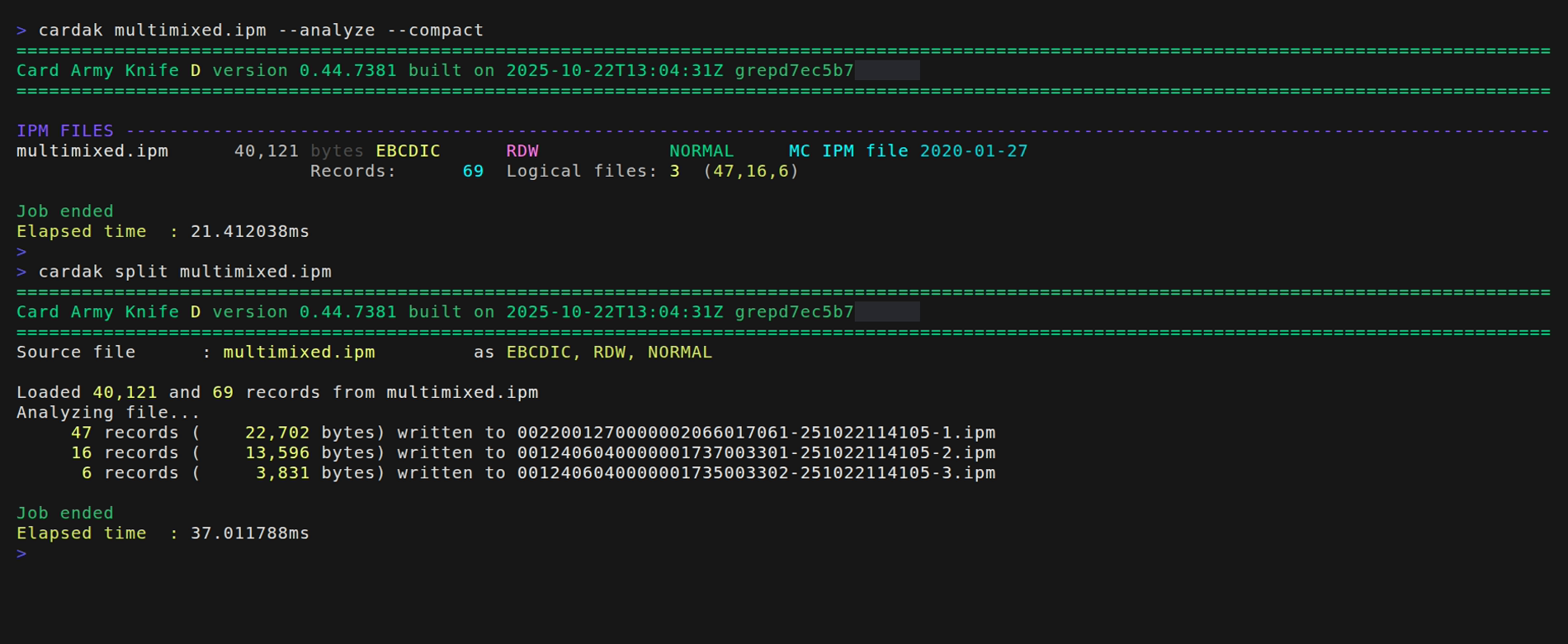
In this example we see that the file contains three logical files containing 47, 16 and 6 records each. So three separate files will be generated with the names as explained before and that contain the corresponding number of records each.