VALIDATE
Validates the structure and integrity of an IPM file.
Syntax
$ cardak help validate
usage: cardak validate [<flags>] <files>...
Validate the IPM files
Flags:
--help Show context-sensitive help (also try --help-long and --help-man).
-v, --verbose Add more information displayed on some commands.
--mono Supress color on output.
--ignore Try to ignore some errors and continue processing the file
-W, --width Ignore small terminal width check and force execution
-z, --silent Suppress all output (banner, headers, summary) except the results. Specially useful for DESCRIBE command piped to a search
utility like fzf
-T, --file-type=FILE-TYPE Filter by file type when supplying several files. File types are represented by a single letter as: I-IPM files, M-MPE files
--mcc Check that MCC values are valid (incomplete list, use with caution)
--fail Just display the list of file names that have errors
--pass Just display the list of file names that don't have errors
Args:
<files> List of files to validate.
Description
This command performs a verification of the integrity and correctness of the data contained in an IPM file. It is a more advanced version of the IDENTIFY command when using the --analyze flag, and it is intended to be used in scripts and automation chains.
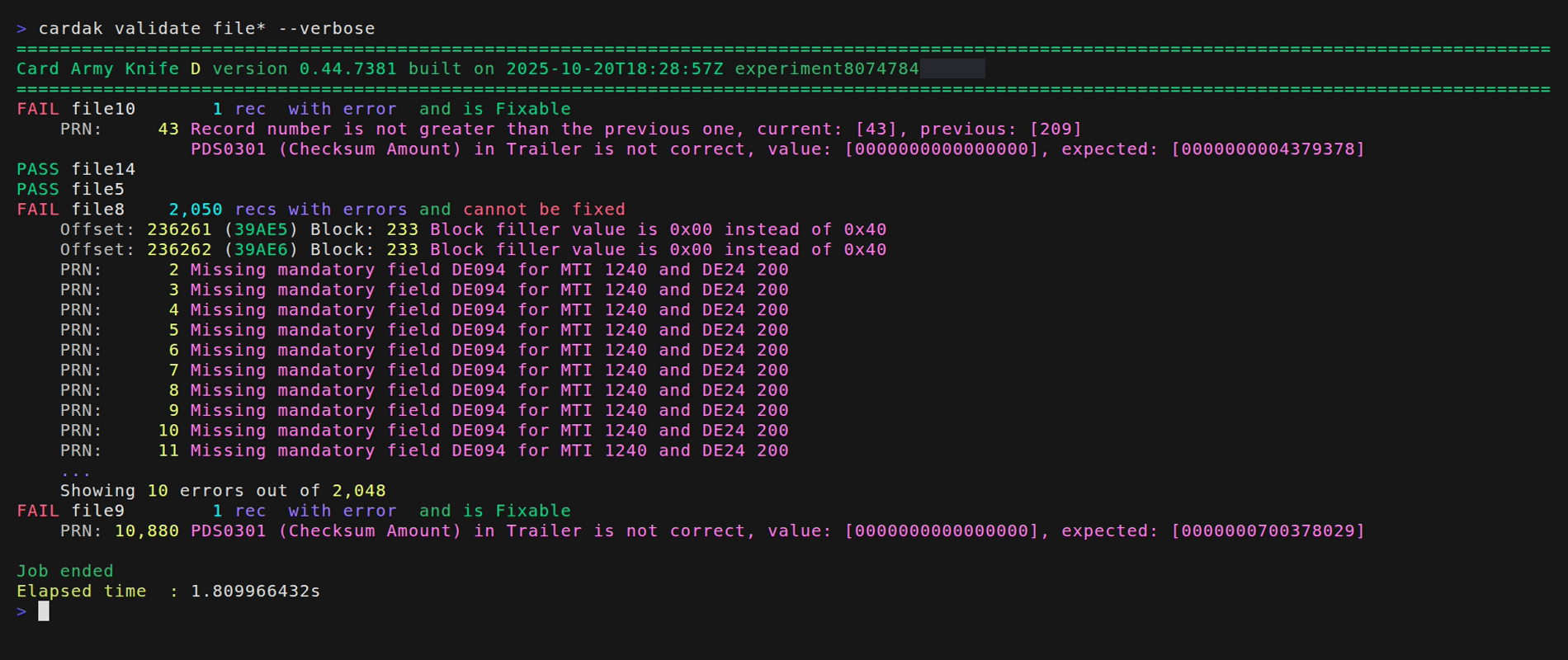
The command analyzes the given files and present the results of each of the files, showing the results as either PASS or FAIL. It also returns to the operating system a value that is zero if all files are correct, or 1 if any of the tested files contain errors, what makes integration with automation software easier.
It also shows if the errors found can be automatically corrected by using the FIX command, or if they cannot be fixed, and it also shows the number of records with errors.
Example:
Available flags
--silent (-z)
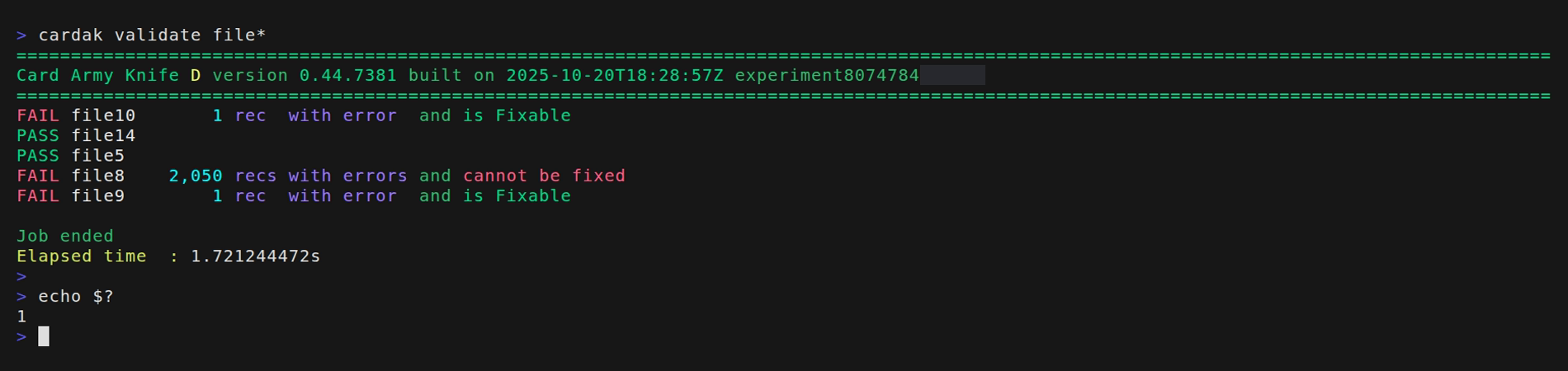
We can use this global flag to get a very compact output that is useful to be parsed by scripts or external processes.

The output consists in a list separated by colons for each file, whe the result of the validation is shown, then the file name, the number of records with errors, and an value indicating if the error can be fixed automatically or not.
--pass
If se use this flag, only the list of files that passed the validations is shown in the output.
--fail
This flag is the opposite to the previous one, and it only displays a list of files with errors.
These flags can be useful in automation systems in order to take actions like moving files into different folders or send alerts depending on the validation status of the files.
Example:

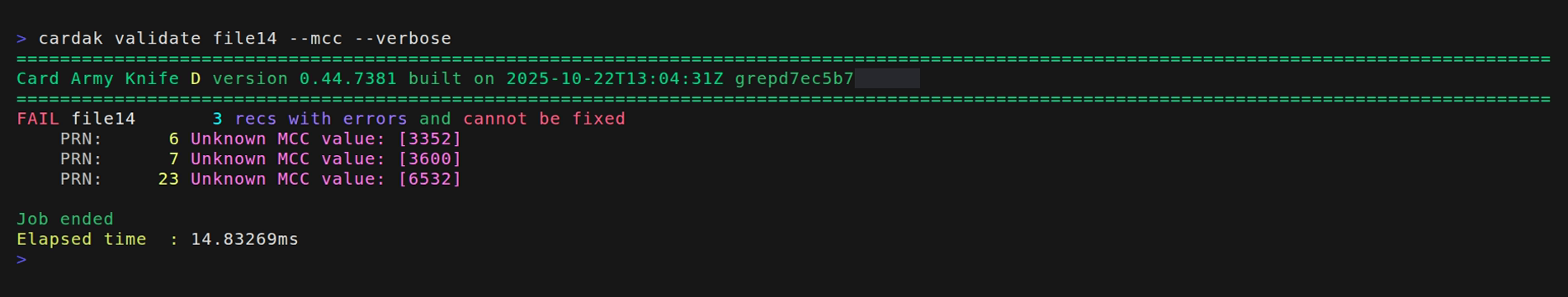
--mcc
This flag is experimental and it can still present false positives. The idea is to verify that the values of the MCC present in the file are valid.
The problem is that this list of MCC varies periodicall and the option to load updated lists of values for the MCC is still not implemented. This is usually done by processing a MPE file, but it can help to display the suspicious values and then decide if they are correct or not.
Example:
--verbose
If we want to see more details about the errors found, we can use this flag and we will se more details about the errors, showing the record number, description of the error and if it is possibe to be fixed automatically.